Mastering the Challenges of the Digital Age in Corporate Management
The build-up of PresentationLoad’s IT portfolio
Bring Your own Device, Data Warehouse and Big Data
Do you seek the possibility of giving your employees a chance to use their own mobile devices inside your company? Does the data flood of your company need to be condensed? Do you want to be able to make smarter and faster decisions and see trends even before they occur?
Information technology isn’t getting more and more important, it’s already an inherent part of our surrounding, our everyday life and thus, a modern corporate process. The bigger a company is, the more significant the possibilities are of maximizing its profit by using IT and the bigger the influence information technology solutions can have on the basics of corporate decision making processes. Even small businesses may benefit from employee satisfaction and operative efficiency increase.
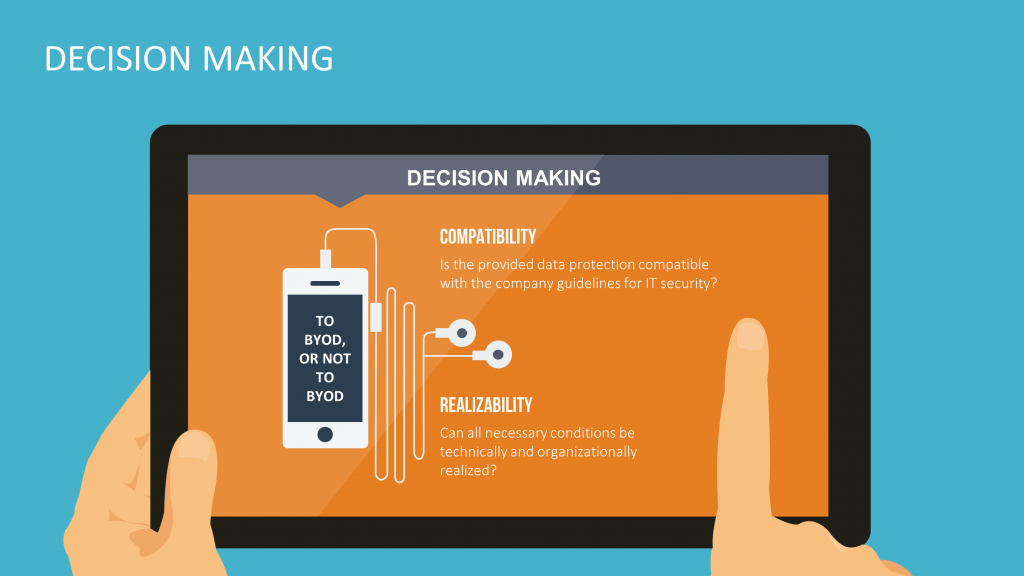
Bring Your own Device – the Heterogeneity of IT Landscapes

The digital world is cluttered with most diverse devices and various operating systems, mostly adapted to the purpose of their application. If you want to allow employees to use their own devices within corporate information technology, many questions arise such as legal issues concerning data protection and privacy, as well as maintenance, services and more.
There is no plain answer to “bring your own device,” “BYOD” in short, because the corporate landscape is as versatile as information technology itself. The solution lies in concentrating on a series of leading questions to derive Pros and Cons, as well as the accruing overvalue and the specific implementation draft for the company.
As for example, one company may be willing to take on maintenance charges, while another provides employee-devices entirely and yet another leaves this aspect completely in the employee’s hands, only to care about questions concerning data security, while benefiting from productivity increase through mobility.
Data Warehouse – a Storehouse for Company’s Data
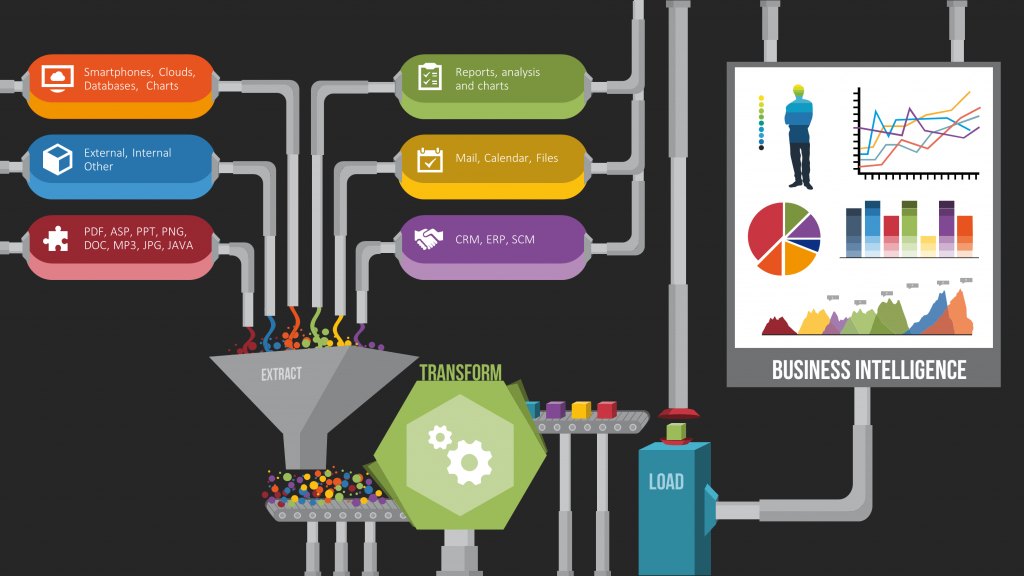
To put it simply, a data warehouse is a database where all relevant data sources of a company are joined. The concept is based on extraction and transformation of existing databases, operational systems, as well as single files and their unification in a composite format.
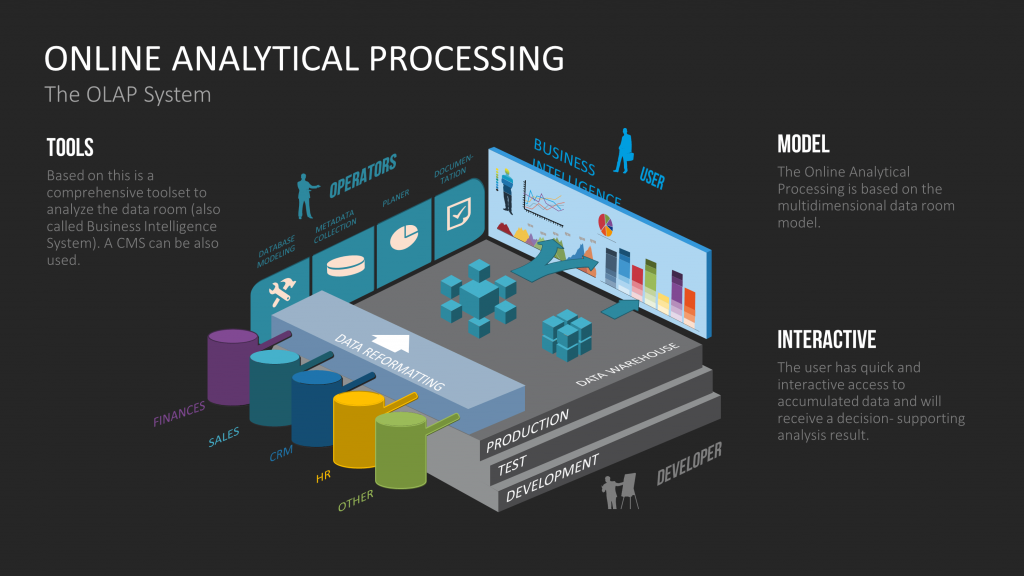
By the use of “Online Analytical Processing,” “OLAP” in short, data are further aggregated and analysed in several steps, with the objective of answering queries placed by a user. An example may be the sales figures of a given product, at a given place, and in a given time period. Finally, the user may change the time period and the related information will be appropriately scaled.
The presentation method should be as assessable and manageable as possible. Additionally, statistical prognosis is possible in a data warehouse by using data mining processes. The more complex possible queries are in a data warehouse, the more accurate certain details of business divisions like marketing and sales can be portrayed.
Hence, the data warehouse grows to be a wide-ranging decision aid for the management of the company. A disadvantage of the data warehouse is that firstly, the data is truncated in consequence of unification and secondly they are only received once a day, thus being inadequate of the most current stand.
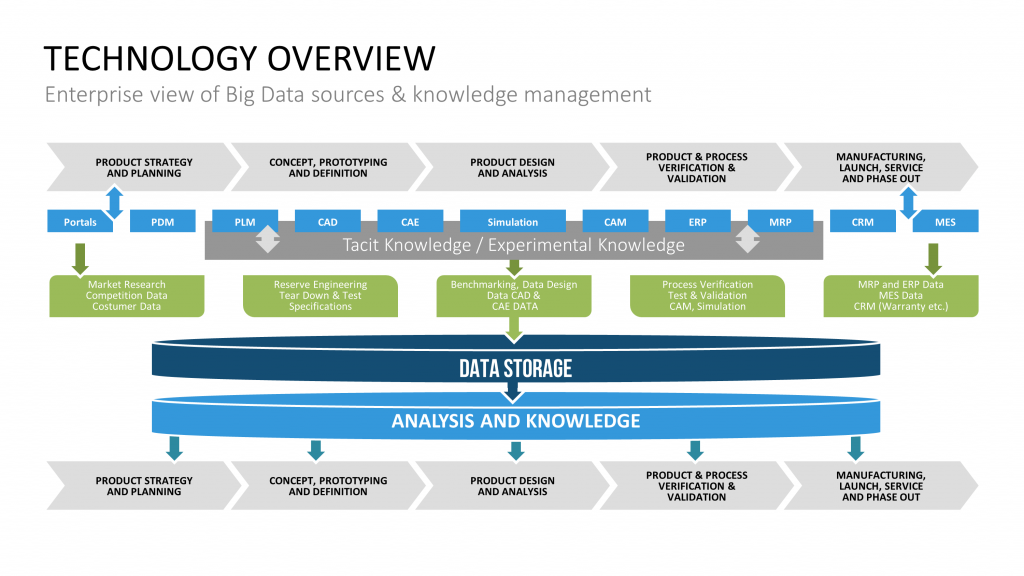
Bid Data – a Harbour at the Sea of Corporate Data
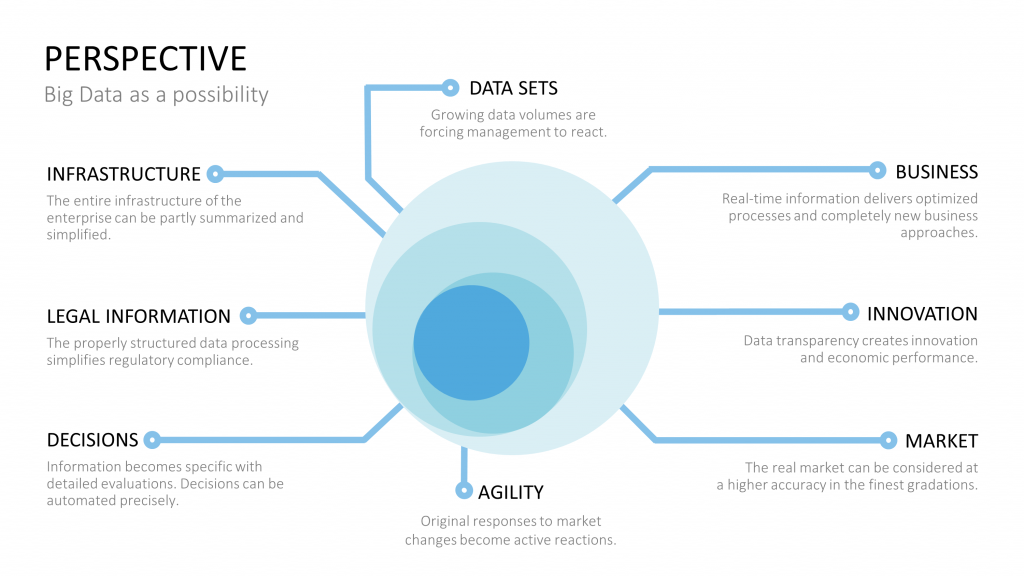
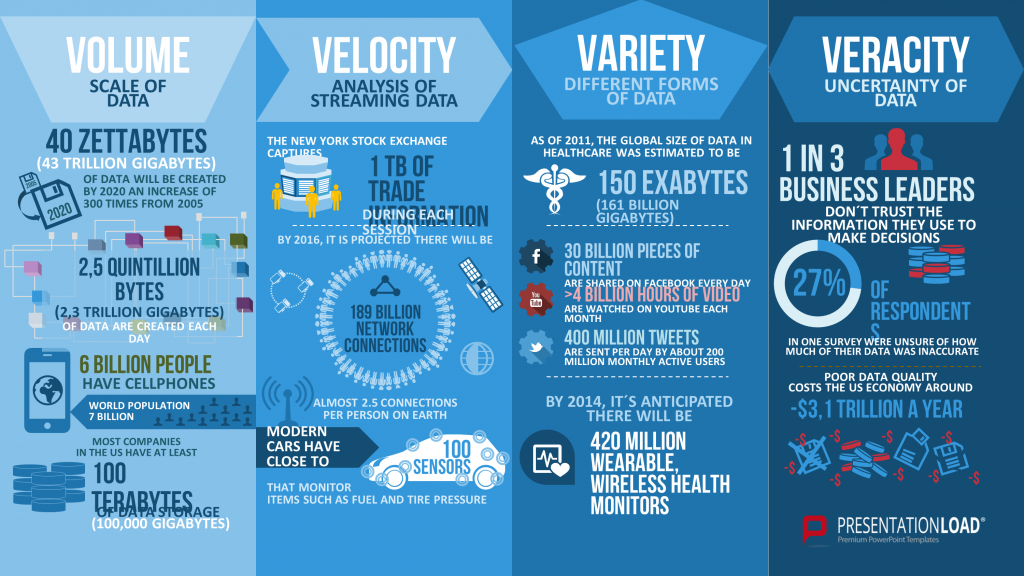
In a case where a corporation produces an outstanding quantity of relevant data, big data may help to gather new insights from on-hand information. Big data, in this case a term for technologies, which assist in collecting and evaluating huge amounts of information. Real time analytics and granularity mostly have priority in this estate. Yet, often such data floods aren’t manageable by usual means anymore.
With the aid of special algorithms, new trends, patterns and unknown correlations are to be found in the acquired information. This fosters innovation and creates unforeseen potential within a company. By monitoring existing parameters in real time for instance, it is possible to recognize production issues at an early stage. Marketing-oriented systems are able to make automatized decisions or serve as detailed data corpus for management decisions.
The main focus of big data lies within the fine-grained data, which allows the most extensive statistical analysis, compared to a data warehouse. At this, one should never underestimate the needed statistical knowledge to operate big data systems and thereby related costs.
The Value of all Technics
All introduced concepts here may benefit a corporation, but the operative word is “may.” This is because all technical systems have their price and their implementation has to be carefully considered by the means of an added value analysis beforehand. For example, it may be quite sensible to target a big data solution, but one should calculate accordingly if on the other hand the value compared to a cheaper data warehouse is minimal.
As a further example, it is usually hard to pass on the use of mobile devices inside a company. However, the usage should take place within a strict policy to prevent the drain of sensitive company data. If this is financially not feasible, at least the usage has to be forbidden as this solution is always preferable to no solution at all. The herewith accompanying losses have then to be accepted. In general, IT decisions are guided by the following.
Five essentials on IT decisions:
- Legal requirements should not be underrated at an early stage of planning, but they should evolve gradually as planning goes on. This is because a completely calculated IT project should not fail in account of planning or generate immense extra costs at the end.
- Security is a key condition when it comes to corporate data as the right information in the wrong hands may cause severe financial damage.
- Technical viability should be in line with the foresaid points because more functionality is usually linked to higher costs. The aim is to build a preferably maintenance-free system, which in fact fulfils its specified functionality.
- The use and monetary value has to be determined definitively in advance. By doing so disappointments at the end of a project can be avoided, parameters can be adjusted during the planning phase and maximum efficiency in the implementation can be achieved.
- The costs have to be set against the added value. Not only short-term investments, like putting into operation, but also long-term costs like operation and maintenance should be carefully considered.
Where We Are Able to Help
Based on frequent requests and more particularly the task of a simple illustration on complex IT contexts, we chose to start an IT portfolio. You want more benefit for your company of modern IT landscape? You are an IT decision-maker? You want to consider your options? We have the solution! IT made clear and simple and to the point.
The available topics “bring your own device,” “data warehouse” and “big data” provide the starting point, where you decide how we go on from here. That is precisely why we look forward to your criticism, praise, suggestions and your specific topics desired!